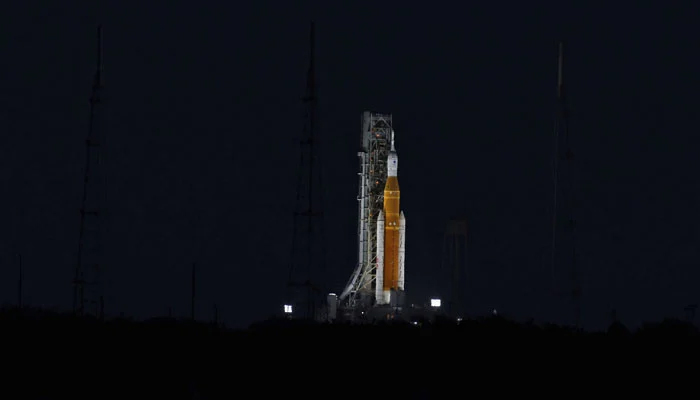
US delays planned return of astronauts to Moon until 2026
Artemis 2, involving crew that doesn't land on surface, has been postponed from later this year to Sep 2025, Nelson says
WASHINGTON: The United States is pushing back its planned return of astronauts to the surface of the Moon from 2025 to 2026, Nasa Administrator Bill Nelson said on Tuesday amid technical challenges and delays.
Artemis, named after the sister of Apollo in Greek mythology, was officially announced in 2017 as part of the US space agency´s plans to establish a sustained presence on Earth´s nearest space neighbor, and apply lessons learned there for a future mission to Mars. Its first mission, an uncrewed test flight to the Moon and back called Artemis 1, took place in 2022, after several postponements.
Artemis 2, involving a crew that doesn´t land on the surface, has been postponed from later this year to September 2025, Nelson told reporters.
Artemis 3, in which the first woman and first person of color are to set foot on lunar soil at the Moon´s south pole, should now take place in September 2026.
“Safety is our top priority, and to give Artemis teams more time to work through the challenges,” said Nelson.
Nasa is also looking to build a lunar space station called Gateway where spacecraft will dock during later missions.
Elon Musk´s SpaceX has won the contract for a landing system for Artemis 3 based on a version of its prototype Starship rocket, which remains far from ready. Both of its orbital tests have ended in explosions.
Delays to Starship have knock-on effects because the spacesuit contractor needs to know how the suits will interface with the spacecraft, and simulators need to be built for astronauts to learn its systems.
And the Artemis 1 mission itself revealed technical issues, such as the heat shield on the Orion crew capsule eroded in an unexpected way, and the ground structure used to launch the giant SLS rocket sustained more damage than expected.
-
 Woman Jailed Over False 'crime In Space' Claim Against NASA Astronaut
Woman Jailed Over False 'crime In Space' Claim Against NASA Astronaut -
 James Van Der Beek’s Close Pal Reveals Family's Dire Need Of Donations
James Van Der Beek’s Close Pal Reveals Family's Dire Need Of Donations -
 Prince William And Harry's Cousins Attend 'Wuthering Heights' Event
Prince William And Harry's Cousins Attend 'Wuthering Heights' Event -
 Hailey Bieber Turns Heads Just Hours After Major Business Win
Hailey Bieber Turns Heads Just Hours After Major Business Win -
 King Charles' Andrew Decision Labelled 'long Overdue'
King Charles' Andrew Decision Labelled 'long Overdue' -
 Timothee Chalamet 'forever Indebted' To Fan Over Kind Gesture
Timothee Chalamet 'forever Indebted' To Fan Over Kind Gesture -
 Columbia University Sacks Staff Over Epstein Partner's ‘backdoor’ Admission
Columbia University Sacks Staff Over Epstein Partner's ‘backdoor’ Admission -
 Ozzy Osbourne's Family Struggles Behind Closed Doors
Ozzy Osbourne's Family Struggles Behind Closed Doors -
 Dua Lipa Claims Long-distance Relationship 'never Stops Being Hard'
Dua Lipa Claims Long-distance Relationship 'never Stops Being Hard' -
 BTS Moments Of Taylor Swift's 'Opalite' Music Video Unvieled: See Photos
BTS Moments Of Taylor Swift's 'Opalite' Music Video Unvieled: See Photos -
 Robin Windsor's Death: Kate Beckinsale Says It Was Preventable Tragedy
Robin Windsor's Death: Kate Beckinsale Says It Was Preventable Tragedy -
 Rachel Zoe Shares Update On Her Divorce From Rodger Berman
Rachel Zoe Shares Update On Her Divorce From Rodger Berman -
 Kim Kardashian Officially Takes Major Step In Romance With New Boyfriend Lewis Hamilton
Kim Kardashian Officially Takes Major Step In Romance With New Boyfriend Lewis Hamilton -
 YouTube Tests Limiting ‘All’ Notifications For Inactive Channel Subscribers
YouTube Tests Limiting ‘All’ Notifications For Inactive Channel Subscribers -
 'Isolated And Humiliated' Andrew Sparks New Fears At Palace
'Isolated And Humiliated' Andrew Sparks New Fears At Palace -
 Google Tests Refreshed Live Updates UI Ahead Of Android 17
Google Tests Refreshed Live Updates UI Ahead Of Android 17




