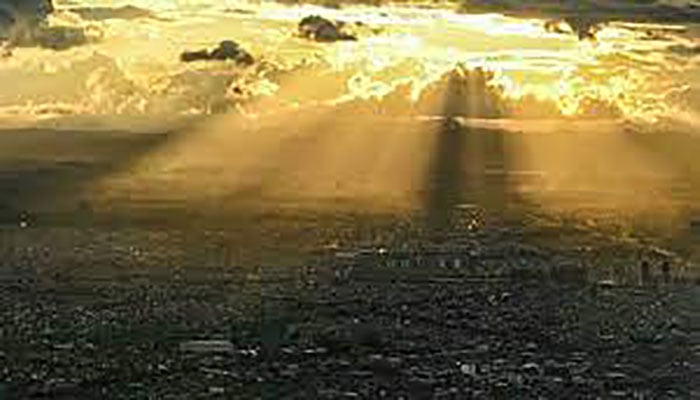
Dimming Sun’s rays should be off-limits, say experts
Planetary-scale engineering schemes designed to cool Earth’s surface and lessen the impact of global heating are potentially dangerous and should be blocked by governments, more than 60 policy experts and scientists said on Monday.
Even if injecting billions of sulphur particles into the middle atmosphere -- the most hotly debated plan for so-called solar radiation modification (SRM) -- turned back a critical fraction of the Sun’s rays as intended, the consequences could outweigh any benefits, they argued in an open letter.
"Solar geoengineering deployment cannot be governed globally in a fair, inclusive and effective manner," said the letter, supported by a commentary in the journal WIREs Climate Change.
"We therefore call for immediate political action from governments, the United Nations and other actors to prevent the normalisation of solar geoengineering as a climate policy option." An increase of 1.1 degrees Celsius above mid-19th century levels has already boosted the intensity, frequency and duration of deadly heat waves, droughts and megastorms. The world’s nations have committed to capping the rise in Earth’s surface temperature to 1.5C above mid-19th century levels, but UN-backed scientists have said that threshold will be breached, possibly within a decade.
The failure to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions that drive global heating has led some policy makers to embrace solar geoengineering -- widely dismissed not long ago as more science fiction than science -- in order to buy time for a more durable solution.
It has long been known that injecting a large quantity of reflective particles into the upper atmosphere could cool the planet. Nature sometimes does the same: debris from the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines lowered Earth’s average surface temperature for more than a year.
But the open letter said there are several reasons to reject such a course of action. Artificially dimming the Sun’s radiative force is likely to disrupt monsoon rains in South Asia and western Africa, and could ravage the rain-fed crops upon which hundreds of millions depend for nourishment, several studies have shown.
"Stratospheric sulfate injection weakens the African and Asian summer monsoons and causes drying in the Amazon," the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) said in its most recent scientific assessment.
-
 Andrew, Sarah Ferguson Refuse King Charles Request: 'Raising Eyebrows Inside Palace'
Andrew, Sarah Ferguson Refuse King Charles Request: 'Raising Eyebrows Inside Palace' -
 Adam Sandler Reveals How Tom Cruise Introduced Him To Paul Thomas Anderson
Adam Sandler Reveals How Tom Cruise Introduced Him To Paul Thomas Anderson -
 Washington Post CEO William Lewis Resigns After Sweeping Layoffs
Washington Post CEO William Lewis Resigns After Sweeping Layoffs -
 North Korea To Hold 9th Workers’ Party Congress In Late February
North Korea To Hold 9th Workers’ Party Congress In Late February -
 All You Need To Know Guide To Rosacea
All You Need To Know Guide To Rosacea -
 Princess Diana's Brother 'handed Over' Althorp House To Marion And Her Family
Princess Diana's Brother 'handed Over' Althorp House To Marion And Her Family -
 Trump Mobile T1 Phone Resurfaces With New Specs, Higher Price
Trump Mobile T1 Phone Resurfaces With New Specs, Higher Price -
 Factory Explosion In North China Leaves Eight Dead
Factory Explosion In North China Leaves Eight Dead -
 Blac Chyna Opens Up About Her Kids: ‘Disturb Their Inner Child'
Blac Chyna Opens Up About Her Kids: ‘Disturb Their Inner Child' -
 Winter Olympics 2026: Milan Protestors Rally Against The Games As Environmentally, Economically ‘unsustainable’
Winter Olympics 2026: Milan Protestors Rally Against The Games As Environmentally, Economically ‘unsustainable’ -
 How Long Is The Super Bowl? Average Game Time And Halftime Show Explained
How Long Is The Super Bowl? Average Game Time And Halftime Show Explained -
 Natasha Bure Makes Stunning Confession About Her Marriage To Bradley Steven Perry
Natasha Bure Makes Stunning Confession About Her Marriage To Bradley Steven Perry -
 ChatGPT Caricature Prompts Are Going Viral. Here’s List You Must Try
ChatGPT Caricature Prompts Are Going Viral. Here’s List You Must Try -
 James Pearce Jr. Arrested In Florida After Alleged Domestic Dispute, Falcons Respond
James Pearce Jr. Arrested In Florida After Alleged Domestic Dispute, Falcons Respond -
 Cavaliers Vs Kings: James Harden Shines Late In Cleveland Debut Win
Cavaliers Vs Kings: James Harden Shines Late In Cleveland Debut Win -
 2026 Winter Olympics Snowboarding: Su Yiming Wins Bronze And Completes Medal Set
2026 Winter Olympics Snowboarding: Su Yiming Wins Bronze And Completes Medal Set