Cosmic secrets revealed by solar eclipses throughout history
On April 8, Nasa plans on firing three rockets into the moons shadow
On April 8, North Americans across 15 United States states, Canada, and Mexico will witness a rare total solar eclipse that won’t be happening again for the next 20 years, New Scientist reported.
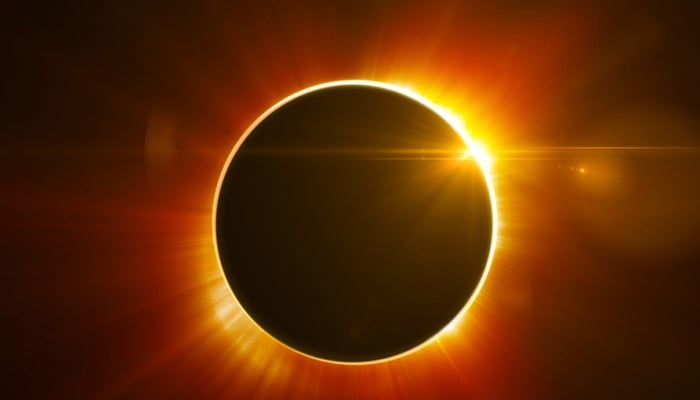
A total solar eclipse is when a moon passes between the sun and the Earth partially or fully blocking the sun's light in some areas.
It occurs about every 18 months providing new insights into the history of the universe and revealing cosmic secrets.
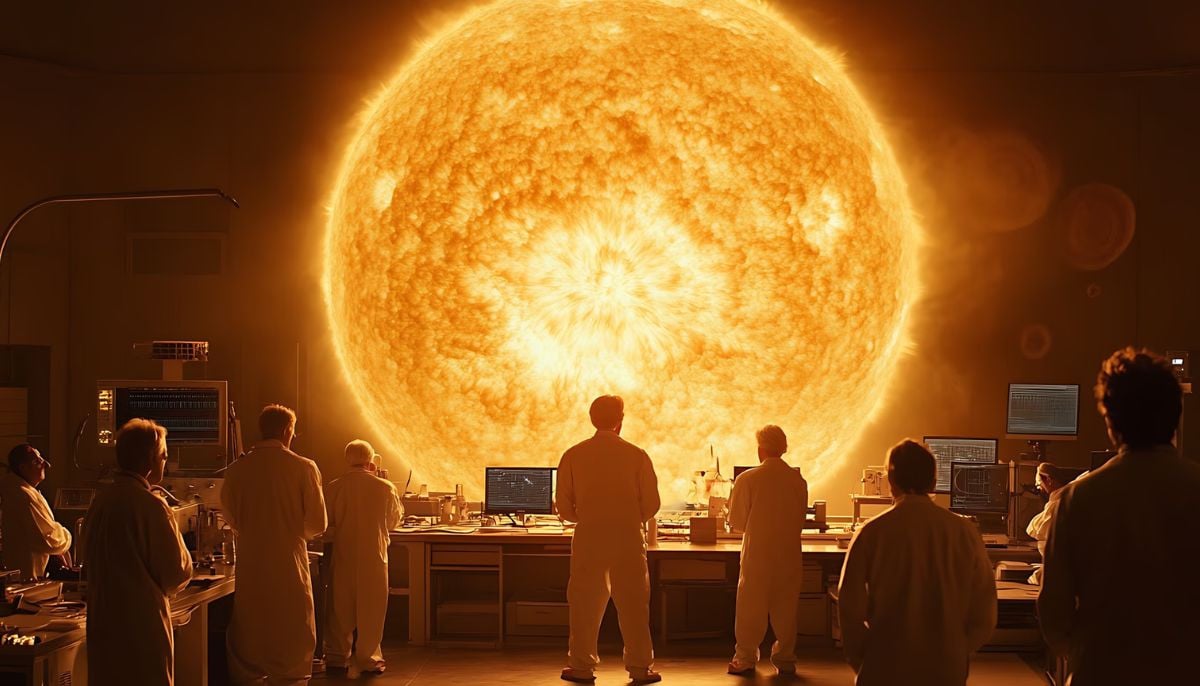
The first known written record of an eclipse dates back almost 3000 years ago. Throughout history, totality is the only time when the sun's outer layer — the corona is visible.
The corona is home to many cosmic secrets; it is a fascinating phenomenon that ejects magnetic fields and blobs of material out into space, also known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
These CMEs are very dangerous as they can damage satellites, the electrical grids, and are extremely harmful to space missions including astronauts.
During a solar eclipse in 1868, scientists first discovered helium using spectroscopy. Spectroscopy is the study and interpretation of electromagnetic spectra. It involves the breaking down of light into different wavelengths to study which elements are present. Helium was the first element ever discovered by studying the skies.
Soon afterward, another element, coronium was found in the corona.
This year when the total solar eclipse passes through North America, Nasa plans on firing three rockets into the sky to unravel more cosmic secrets.
-
Shanghai Fusion ‘Artificial Sun’ achieves groundbreaking results with plasma control record
-
Polar vortex ‘exceptional’ disruption: Rare shift signals extreme February winter
-
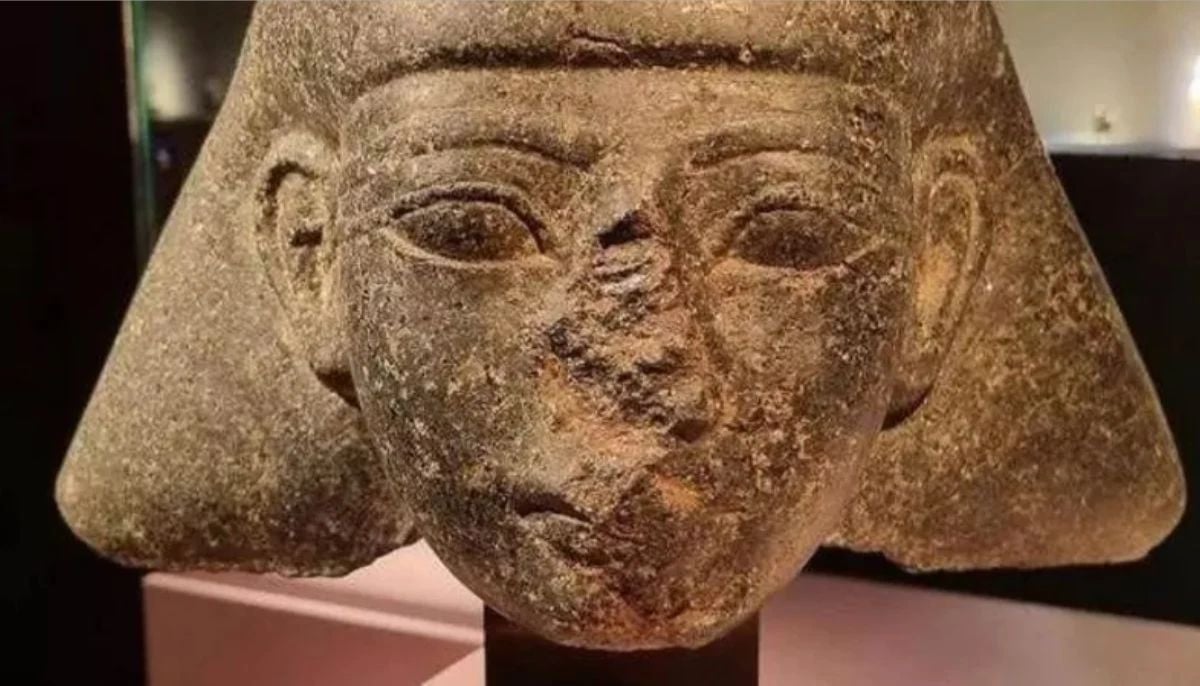
Netherlands repatriates 3500-year-old Egyptian sculpture looted during Arab Spring
-
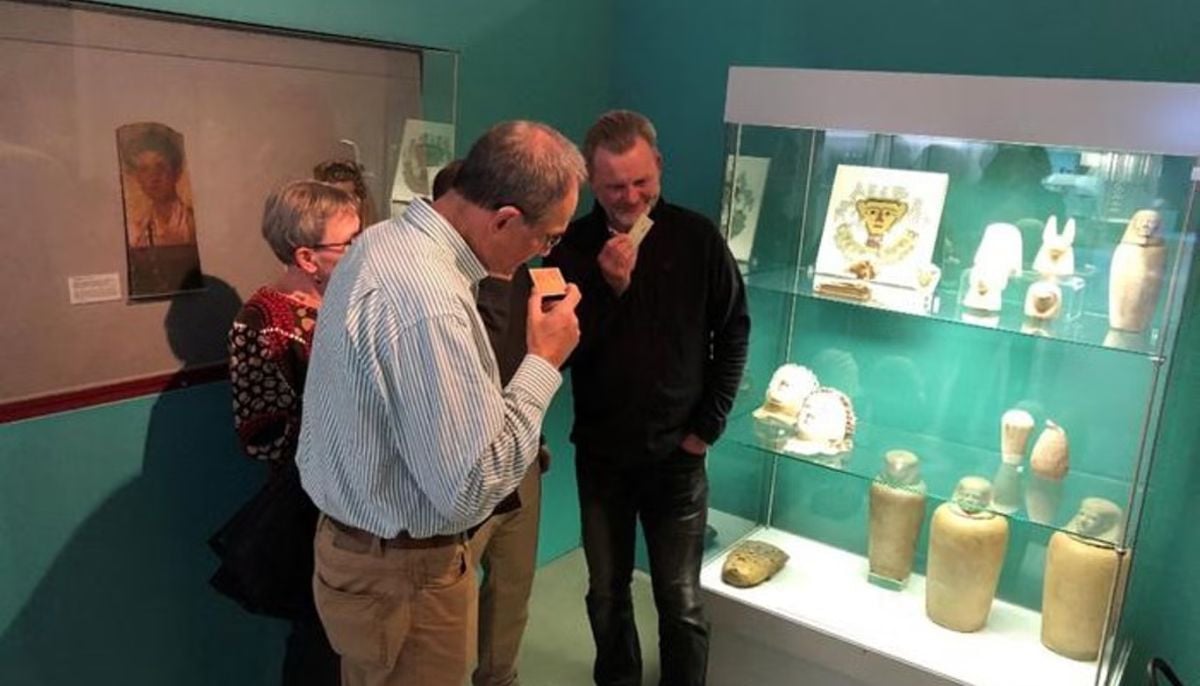
Archaeologists recreate 3,500-year-old Egyptian perfumes for modern museums
-
Smartphones in orbit? NASA’s Crew-12 and Artemis II missions to use latest mobile tech
-
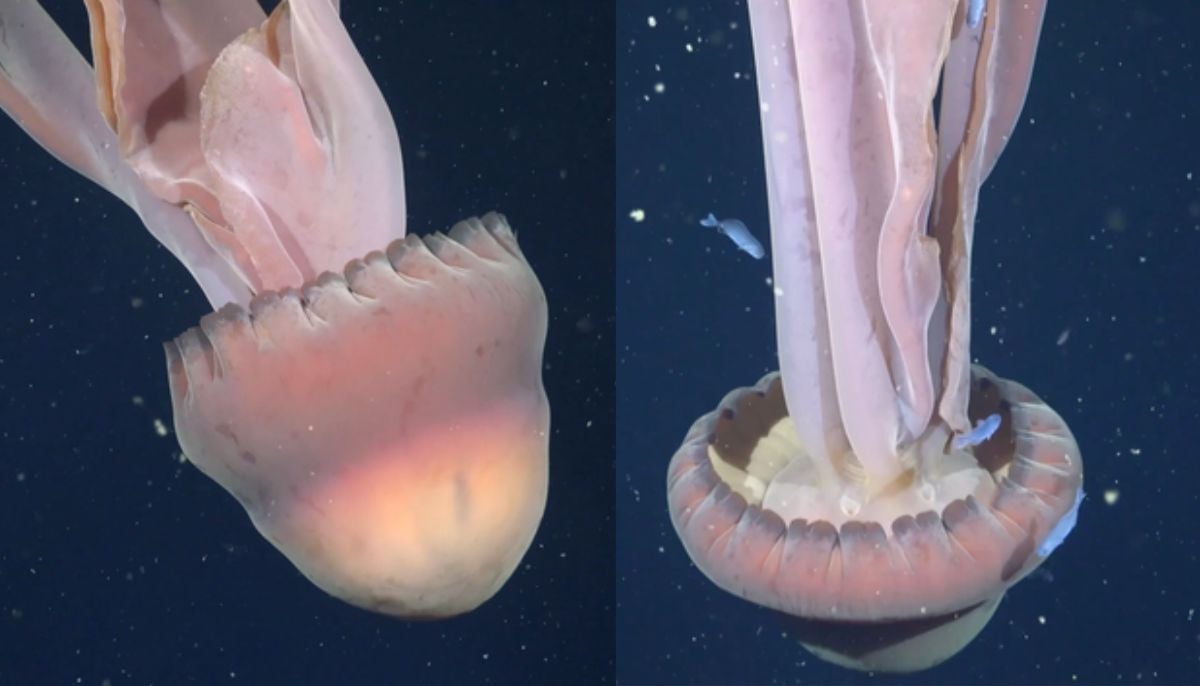
Rare deep-sea discovery: ‘School bus-size’ phantom jellyfish spotted in Argentina
-
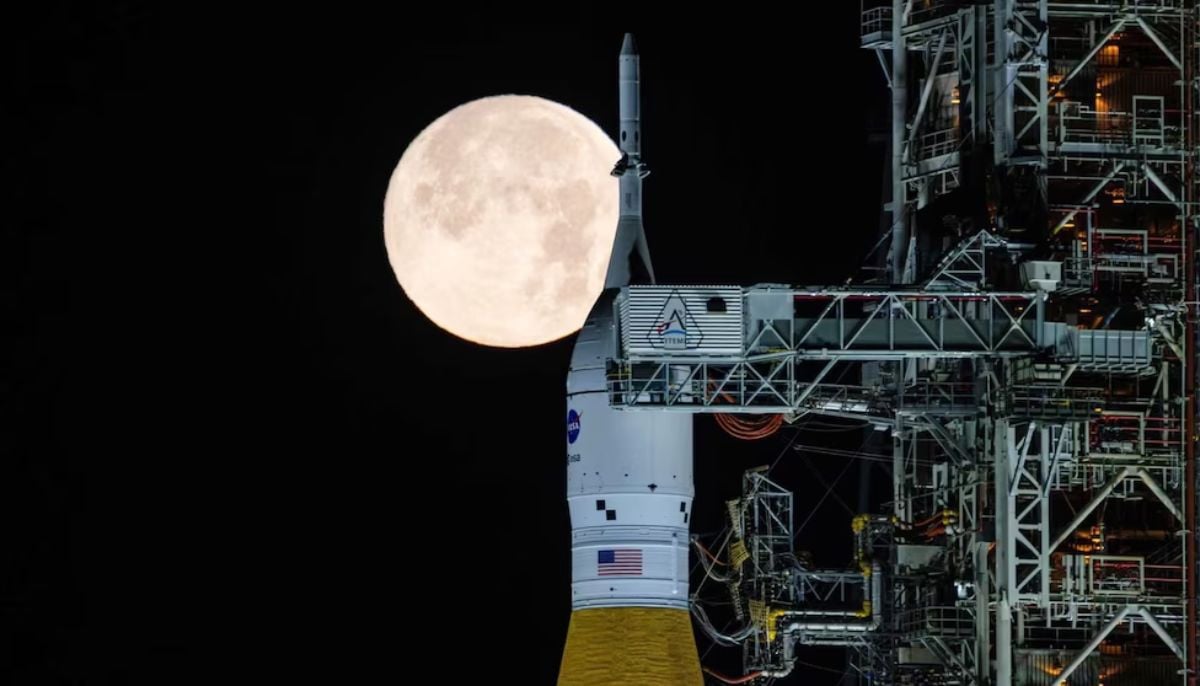
NASA eyes March moon mission launch following test run setbacks
-
February offers 8 must-see sky events including rare eclipse and planet parade