SpaceX Falcon 9 launches 19 Starlink satellites from California
The mission, designated Starlink 13-4, lifted off at 11:32 a.m. on July 31, 2025
SpaceX successfully deployed a Falcon 9 rocket from California’s Vandenberg Space Force Base on Thursday, July 31, 2025, carrying 19 Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit.
The mission titled “Starlink 13-4” took off at 11:32 a.m. PDT (2:35 p.m. EDT) from fog covered Space Launch Complex 4 East (SLC-4E).
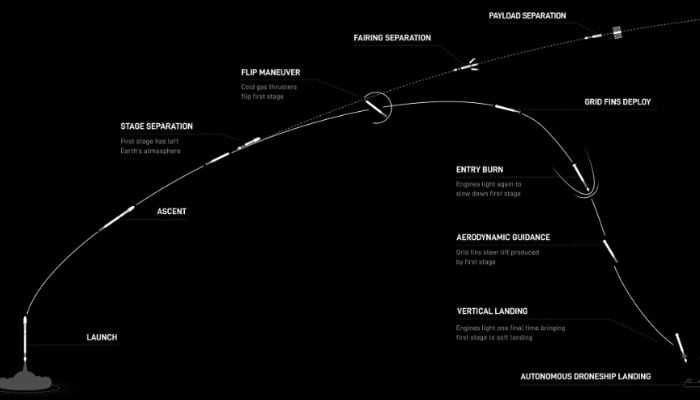
Countdown
00:38:00- SpaceX Launch Director verifies go for propellant load
00:35:00- RP-1 (rocket grade kerosene) loading begins
00:35:00- 1st stage LOX (liquid oxygen) loading begins
00:16:00- 2nd stage LOX loading begins
00:07:00- Falcon 9 begins engine chill prior to launch
00:01:00- Command flight computer to begin final prelaunch checks
00:01:00- Propellant tank pressurization to flight pressure begins
00:00:45- SpaceX Launch Director verifies go for launch
00:00:03- Engine controller commands engine ignition sequence to start
00:00:00- Falcon 9 liftoff
With the confirmation of launching these 19 satellites, concerns have been raised about extra classified payloads possibly hitching a ride.
The company notably omitted second-stage footage that includes the usual payload fairing separation. Such a practice is usually related to undisclosed government satellites.
This suggests additional payloads may have flown alongside the 19 declared Starlink satellites.
Given these circumstances, analysts suggest that the recently deployed satellites could be part of SpaceX’s Starshield program. This initiative is a classified, government-focused satellite constellation designed to enhance national security capabilities.
The Falcon 9 delivered its payloads into a polar orbit at an altitude of 202x193 miles (325x311km), inclined at 97.6 degrees.
The notable feature of the mission is utilizing a veteran booster B1071 that has successfully completed its 27th launch. Featuring a reusable booster is a testament of SpaceX’s reusability milestone.
It was previously used in high-profiled missions such as NROL-87, NROL-85, SARah-1, SWOT, and multiple Starlink deployments.
SpaceX continues to expand its Starlink constellation, now comprising thousands of satellites providing global internet coverage.
Meanwhile, the potential presence of classified payloads highlights the company’s growing role in national security space missions.
-
BAFTA winner Robert Aramayo defends director's racial slurs amid tics
-
Kim Kardashian obsessed TV star 'Lip King' breathes his last at 32
-
Why Elon Musk believes guardrails or kill switches won’t save humanity from AI risks
-
Tom Cruise, Nicole Kidman mend their relationship following the murder of Rob Reiner, wife Michelle Reiner?
-
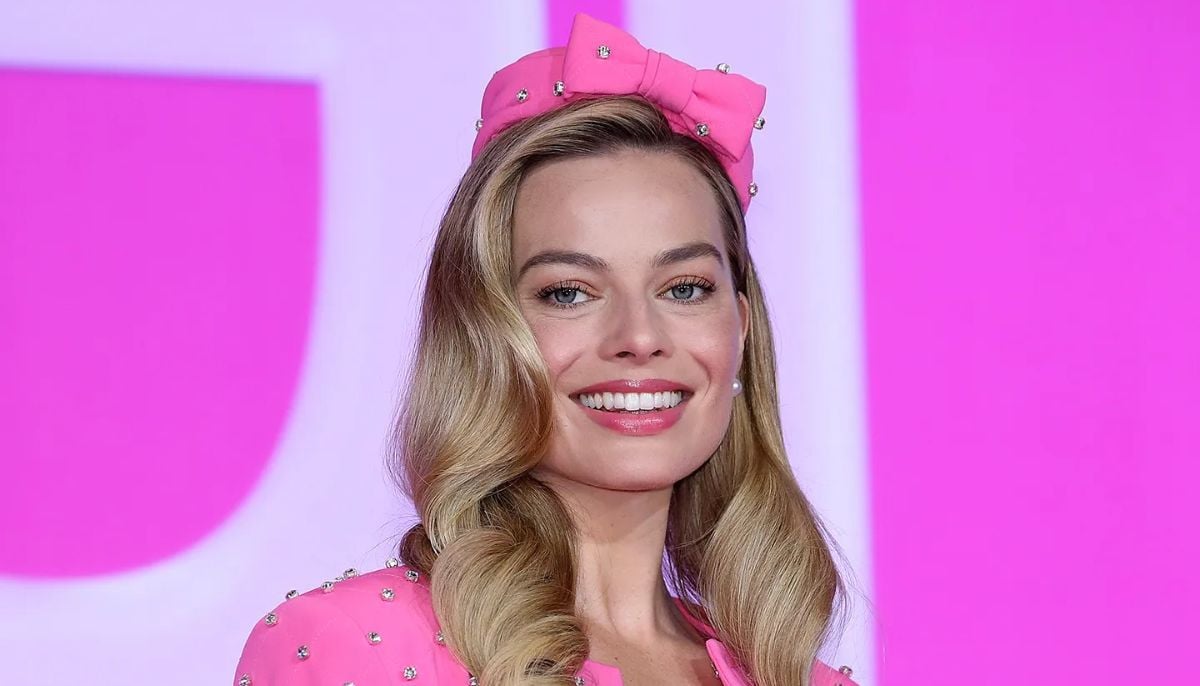
Margot Robbie fears being dubbed a 'dumb blonde' due to major reasons: 'Hates the idea'
-
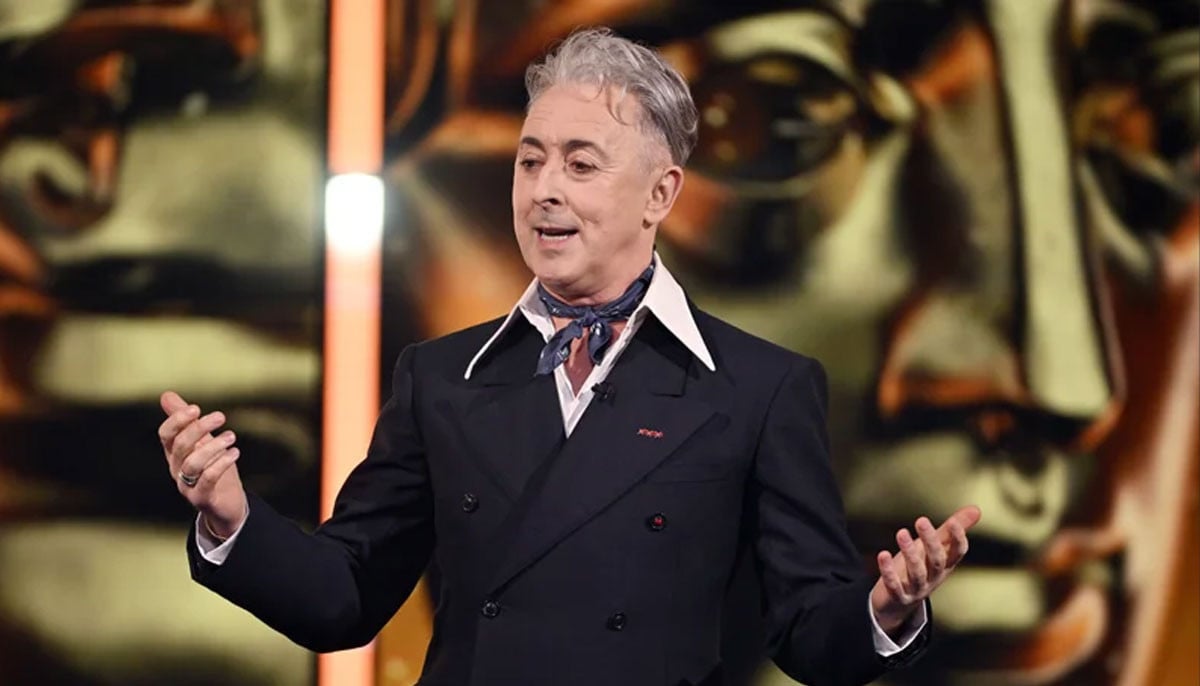
Host Alan Cumming thanks BAFTAs audience for understanding after Tourette’s interruption from activist
-
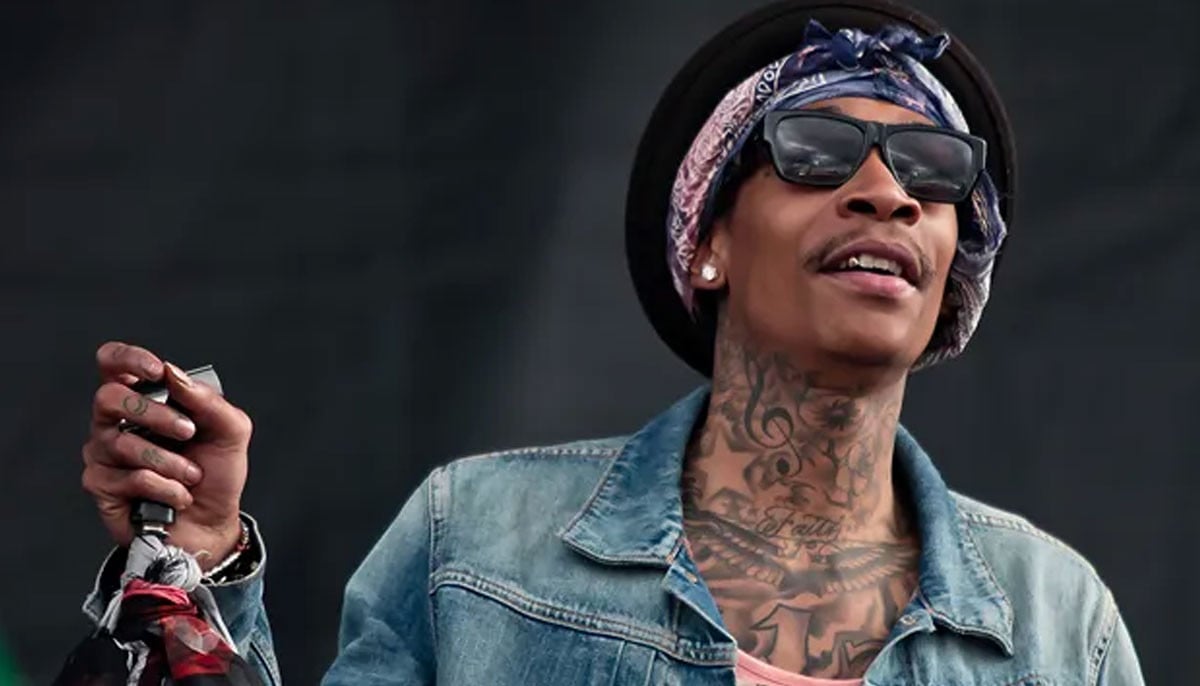
Wiz Khalifa reveals unconventional birthday punch tradition with teenage son in new video
-
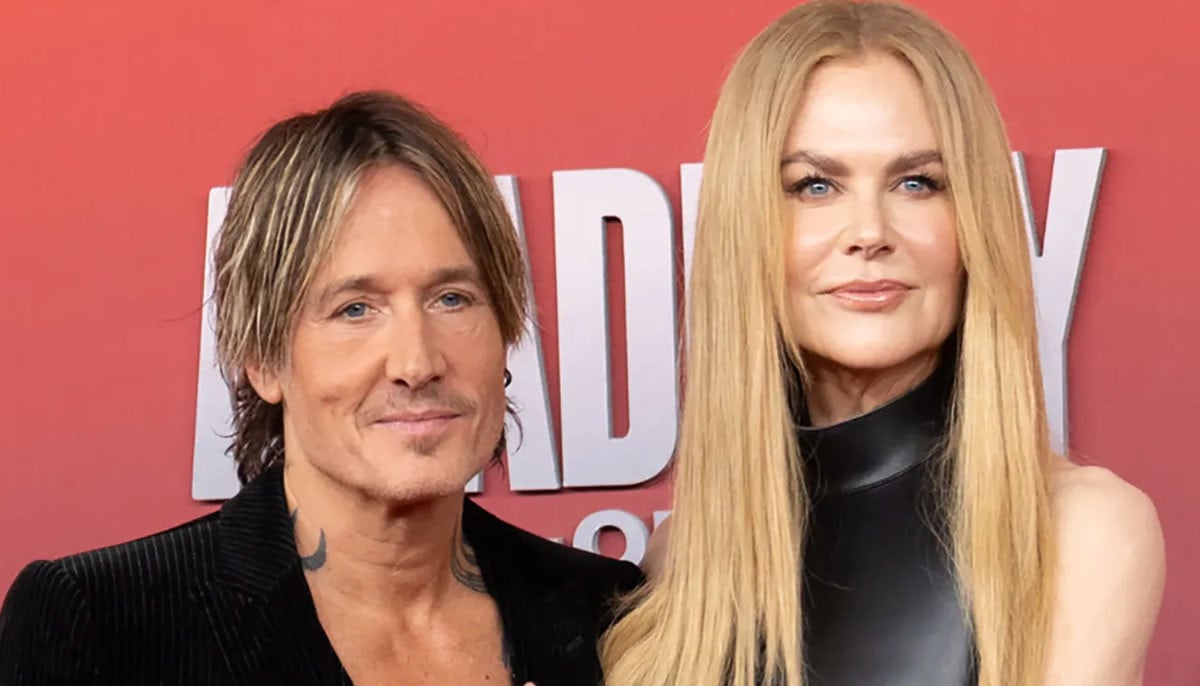
Keith Urban fires entire management team after divorcing Nicole Kidman