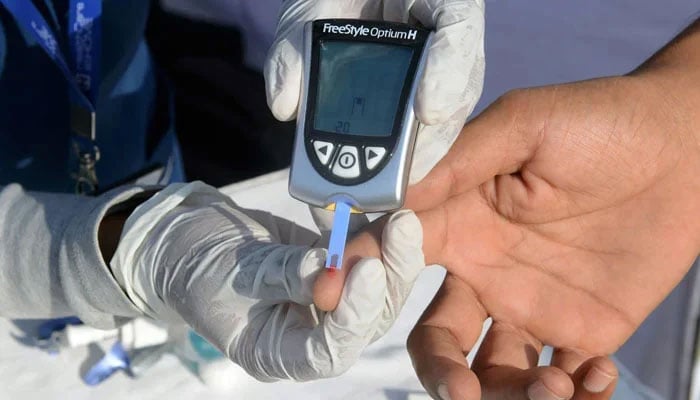
Diabetics while fasting should monitor blood sugar level regularly
Rawalpindi: Patients with diabetes falling in the third category of the disease who take insulin for controlling blood sugar and the diabetics suffering from wild fluctuations in blood sugar must consult a qualified physician while opting for regular fasting in the holy month of Ramazan as they may suffer both the short and long-term complications.
Wild blood sugar fluctuations or swings means 300 milligrams per deciliter one day and 50 mg/dl the next day and this condition, according to health experts, may make a diabetic unable to fast because a diabetic cannot risk lowering of blood sugar too much or getting it much higher as the conditions can seriously affect his or her health. Patients experiencing unpredictable swings in blood sugar (glucose) levels need extraordinary care to avoid complications while fasting.
Also, the pregnant women with a history of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and patients with a history of a diabetes complication called ketoacidosis should not fast without prior consultation with their physicians. Medically, in diabetic ketoacidosis, the blood becomes highly acidic as a result of dehydration and excessive ketone (acid) production. The serious condition can make a patient violently ill and can cause death.
The diabetics with well-controlled diabetes may have less or no health risk while fasting in Ramazan however experts say that all the diabetics while fasting should follow a proper diet plan after taking guidance from a qualified physician and must monitor their blood sugar levels regularly in Ramazan.
Experts believe that the patients with persistent uncontrolled diabetes while fasting may have adverse effects on health. In such patients, the HbA1c level increases that is predictive of associated complications of both short and long-term nature. Such patients may also suffer from metabolic disorders.
It is important that diabetics on insulin stop using it during a fast that may be applicable for some patients with Type 2 diabetes, but for Type 1, life of a patient mostly depends on it, and such patient can not stop basal insulin. In Type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin while in Type 2, the pancreas usually produces some insulin.
Studies reveal that the risk for hypoglycaemia (lowering of blood sugar) is 4.7 times greater than normal during fasting in those with Type 1 diabetes and 7.5 times greater than normal in those with Type 2 diabetes. Regular fasting among the patients with persistent high blood sugar levels may cause damage to kidneys.
Experts say that the lowering of blood sugar level is a greater concern while fasting but high blood sugar can also occur and it is frequent monitoring that reduces the risk of both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
According to experts, the diabetic cases are considered unique in nature so every diabetic should have an advice from his or her physician while opting for regular fasting. Also, a physician may make a change in schedule of medicines of a patient to avoid complications during fasting in Ramazan and it can be possible only when the patient informs the physician well in time of his intentions of opting for fasting.
In simple words, the patients who control sugar level by adopting life interventions like exercise and walk do not have any complications while fasting; however they should follow doctor’s advice regarding diet. The diabetics who use oral hypoglycaemic medicines (tablets) to control sugar level in their blood can fast only if they have no complications of the disease. The patients who take insulin for controlling blood sugar fall in the third category and such patients being more diabetic may develop complications due to a little carelessness and medically fasting in them is not recommended.
Diabetics should avoid ‘Sharbats’ and sweet substances like ‘Jalebis’ at the time of iftar, as the sweet substances may cause hyperglycaemic peaks (sudden shooting up of sugar level) which is dangerous for patients. At the time of ‘Sehr’, a diabetic should take plain leaf of bread (chapati not paratha) preferably with yogurt, milk, vegetable curry, pulses or egg however he should avoid jams and marmalade. A diabetic going for fasting may add food with high protein including fish, meat, chicken, pulses and eggs to his diet plan but after taking advice from a physician.
-
 JoJo Siwa Shares Inspiring Words With Young Changemakers
JoJo Siwa Shares Inspiring Words With Young Changemakers -
 James Van Der Beek Loved Ones Breaks Silence After Fundraiser Hits $2.2M
James Van Der Beek Loved Ones Breaks Silence After Fundraiser Hits $2.2M -
 Disney’s $336m 'Snow White' Remake Ends With $170m Box Office Loss: Report
Disney’s $336m 'Snow White' Remake Ends With $170m Box Office Loss: Report -
 Travis Kelce's Mom Donna Kelce Breaks Silence On His Retirement Plans
Travis Kelce's Mom Donna Kelce Breaks Silence On His Retirement Plans -
 Premiere Date Of 'Spider-Noir' Featuring Nicolas Cage Announced
Premiere Date Of 'Spider-Noir' Featuring Nicolas Cage Announced -
 Pedro Pascal's Sister Reveals His Reaction To Her 'The Beauty' Role
Pedro Pascal's Sister Reveals His Reaction To Her 'The Beauty' Role -
 Kate Middleton Proves She's True 'children's Princess' With THIS Move
Kate Middleton Proves She's True 'children's Princess' With THIS Move -
 Paul Anka Reveals How He Raised Son Ethan Differently From His Daughters
Paul Anka Reveals How He Raised Son Ethan Differently From His Daughters -
 'A Very Special Visitor' Meets Queen Camilla At Clarence House
'A Very Special Visitor' Meets Queen Camilla At Clarence House -
 Jodie Turner Smith Shares One Strict Rule She Follows As A Mom
Jodie Turner Smith Shares One Strict Rule She Follows As A Mom -
 Hailey Bieber Reveals KEY To Balancing Motherhood With Career
Hailey Bieber Reveals KEY To Balancing Motherhood With Career -
 Photo Of Jay-Z, Other Prominent Figures With Jeffrey Epstein Proven To Be Fake
Photo Of Jay-Z, Other Prominent Figures With Jeffrey Epstein Proven To Be Fake -
 Hillary Clinton's Munich Train Video Sparks Conspiracy Theories
Hillary Clinton's Munich Train Video Sparks Conspiracy Theories -
 Fans Slam Talk Show Host For 'cringe' Behavior In Chris Hemsworth Interview
Fans Slam Talk Show Host For 'cringe' Behavior In Chris Hemsworth Interview -
 Woman Jailed Over False 'crime In Space' Claim Against NASA Astronaut
Woman Jailed Over False 'crime In Space' Claim Against NASA Astronaut -
 James Van Der Beek’s Close Pal Reveals Family's Dire Need Of Donations
James Van Der Beek’s Close Pal Reveals Family's Dire Need Of Donations