Hubble discovers ‘Cloud 9,’ strange cosmic object with no stars
Astronomers spot rare dark matter cloud with gas but no stars, offering new clues about galaxy formation
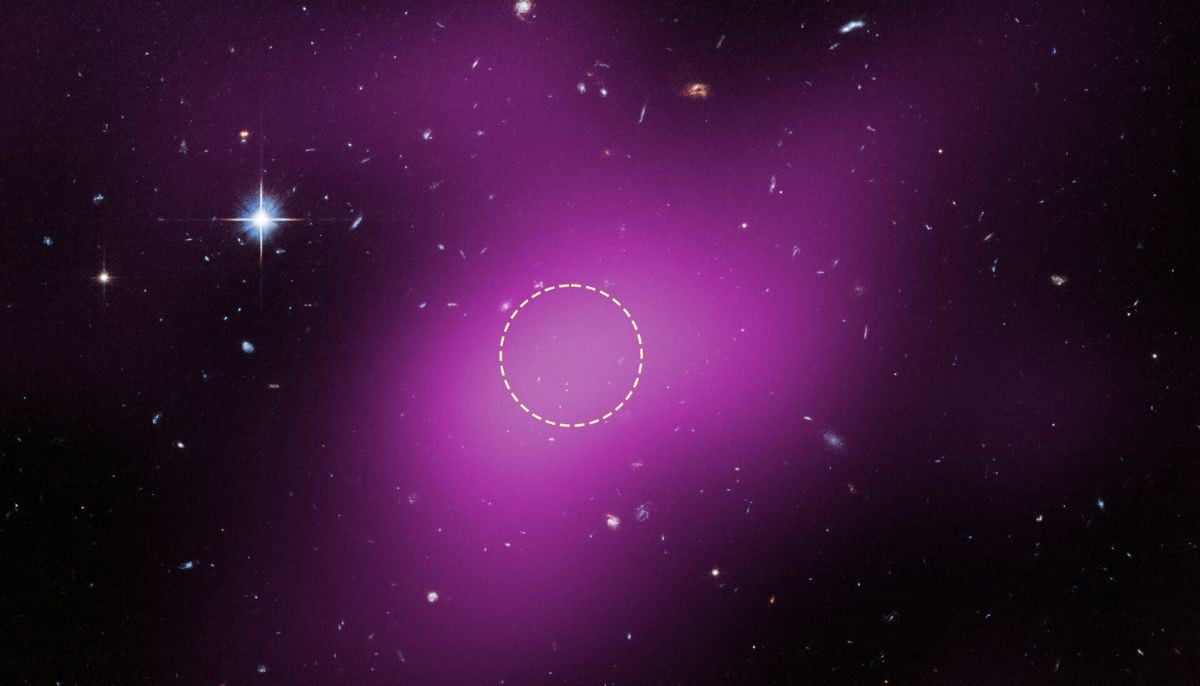
Using the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have discovered a new type of cosmic object nicknamed Cloud 9, located about 14 million light-years from Earth near the outer edges of the spiral galaxy Messier 94 (M94).
The discovery answers what the object is, where it lies, who found it, how it was detected, when it was confirmed, and why it matters for understanding dark matter and galaxy formation.
Cloud 9 findings
Cloud 9 represents a gas cloud, dominated by dark matter, without stars, with scientists classifying it as a Reionization-Limited HI Cloud (RELHIC). As the AURA/Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) team points out, this find offers a rare window into dark matter, the invisible 85% of the universe's mass that radiates no light and is notoriously hard to detect directly.
Cloud 9 contains hydrogen gas, the raw material in many astrophysical environments which would lead to star formation; yet, such a process never took off. It is that very absence that makes Cloud 9 so valuable for researchers studying dark matter halos, failed galaxies, and the early building blocks of the cosmos.
Alejandro Benitez-Llambay of Milano-Bicocca University calls Cloud 9 a "failed galaxy". He cites the lack of stars as supportive of long-held ideas about how galaxies begin as dark matter clumps that sometimes never quite mature into full galaxies.
Deep imaging with the Hubble Space Telescope allowed astronomers to verify that there are truly no hidden stars in Cloud 9, that it isn't some sort of faint dwarf galaxy in disguise.
The dark matter mass of Cloud 9 is estimated to be around five billion solar masses, but the mass of the visible gas that it contains is rather modest. The discovery gives an inkling that many more galaxies without stars may well exist in the neighbourhood.
-
What happens if ChatGPT gains access to your financial accounts? Experts are alarmed
-
Anthropic seeks legal pause on Pentagon supply-chain risk decision: Here’s why
-
'AI washing' or real shift? Atlassian cuts 1,600 jobs in latest tech shake-up
-
Experts predict AI will trigger biggest shift in mathematics history
-
China’s cyber agency raises concerns over OpenClaw AI
-
WhatsApp plans major change for younger users
-
Musk unveils Tesla, xAI joint project ‘Macrohard’ amid advanced AI push
-
Nvidia secures $2 billion deal with AI cloud provider Nebius