'Nightmarish' fossil of 66-million-year old sea lizard discovered
Khinjaria Acuta belongs to family of monasaurs which are connected to today’s anacondas and Komodo dragons
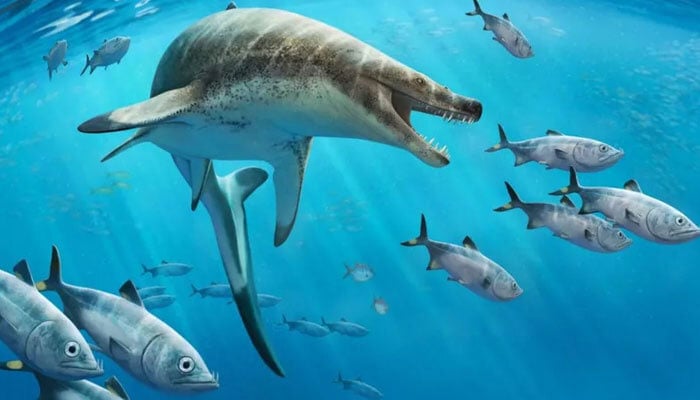
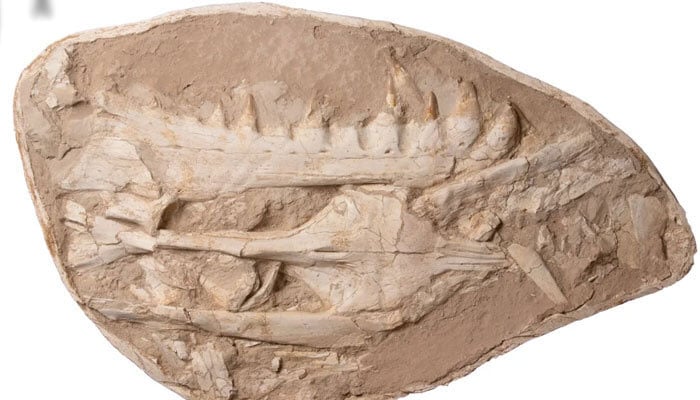
In a scientific marvel, a fossil of a sea lizard species named "Khinjaria Acuta" has been discovered off the coast of Morocco. It is believed to have lived 66 million years ago alongside dinosaurs such as Tyrannosaurus rex, the BBC reported.
Khinjar, meaning dagger in Arabic, and Acuta, meaning sharp in Latin, perfectly describe the species, as researcher Dr Nick Longrich from the University of Bath, who led the study published in the Journal Cretaceous Research, wrote that the creature looked "freakish" and had "a demon's face and teeth like knives."
He said that its teeth and strong jaw gave the creature a "nightmarish appearance" and "a terrible biting force."
According to researchers, the Khinjaria Acuta belongs to the family of "monasaurs," who are giant marine lizards and are connected to today’s anacondas and Komodo dragons.
It is believed that the lizard species discovered was one of the top predators at the time it lived in the Atlantic Ocean.
As per Longrich, what makes the discovery so "remarkable is the sheer diversity of top predators."
He said, "We have multiple species growing larger than a great white shark, and they're top predators, but they all have different teeth, suggesting they're hunting in different ways.
"Some mosasaurs had teeth to pierce prey, others to cut, tear, or crush. Now we have Khinjaria, with a short face full of huge, dagger-shaped teeth."
-
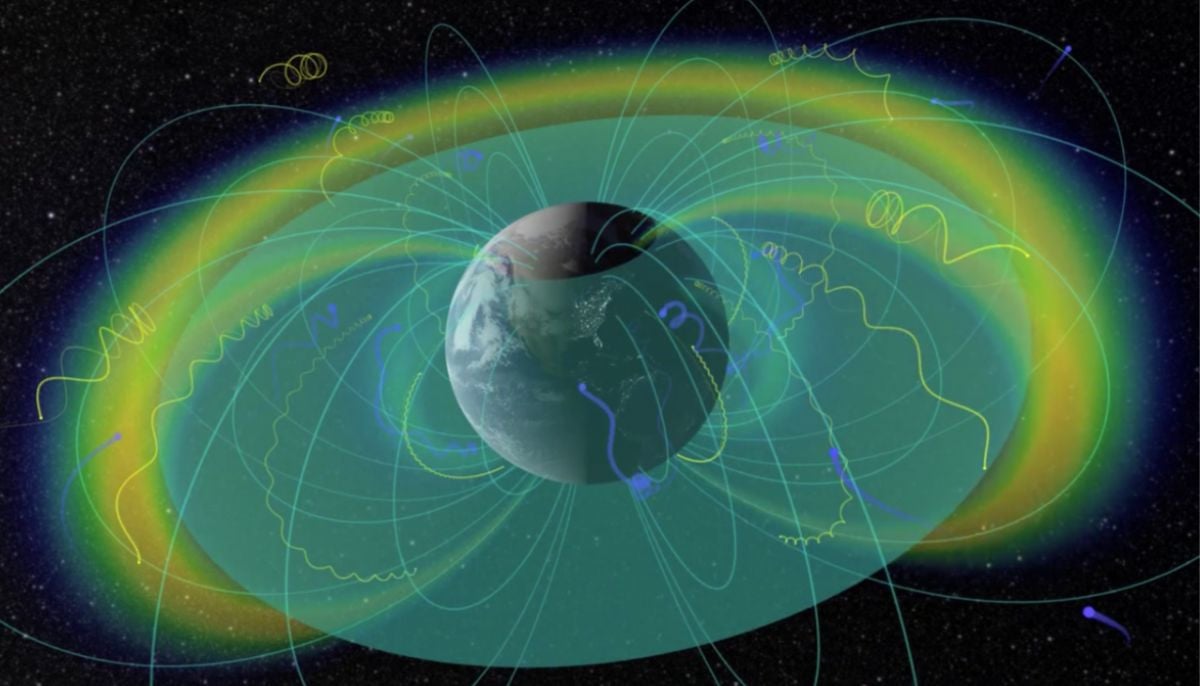
‘Smiling electrons’ discovered in Earth’s magnetosphere in rare space breakthrough
-
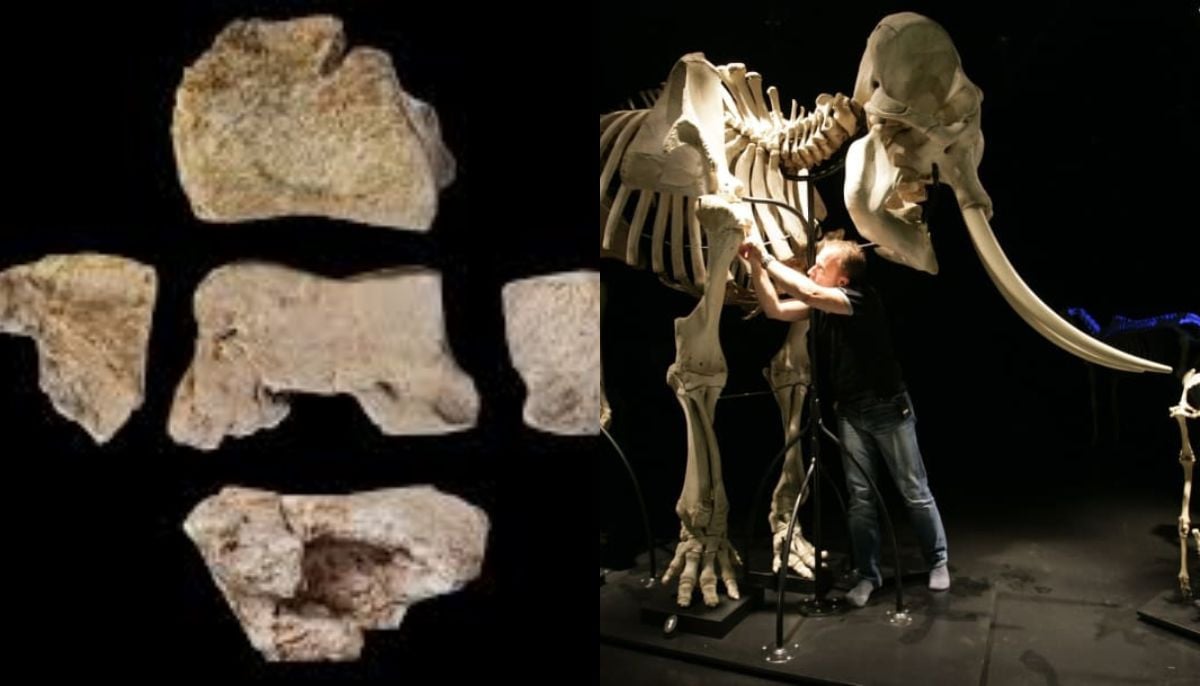
Archaeologists unearthed possible fragments of Hannibal’s war elephant in Spain
-
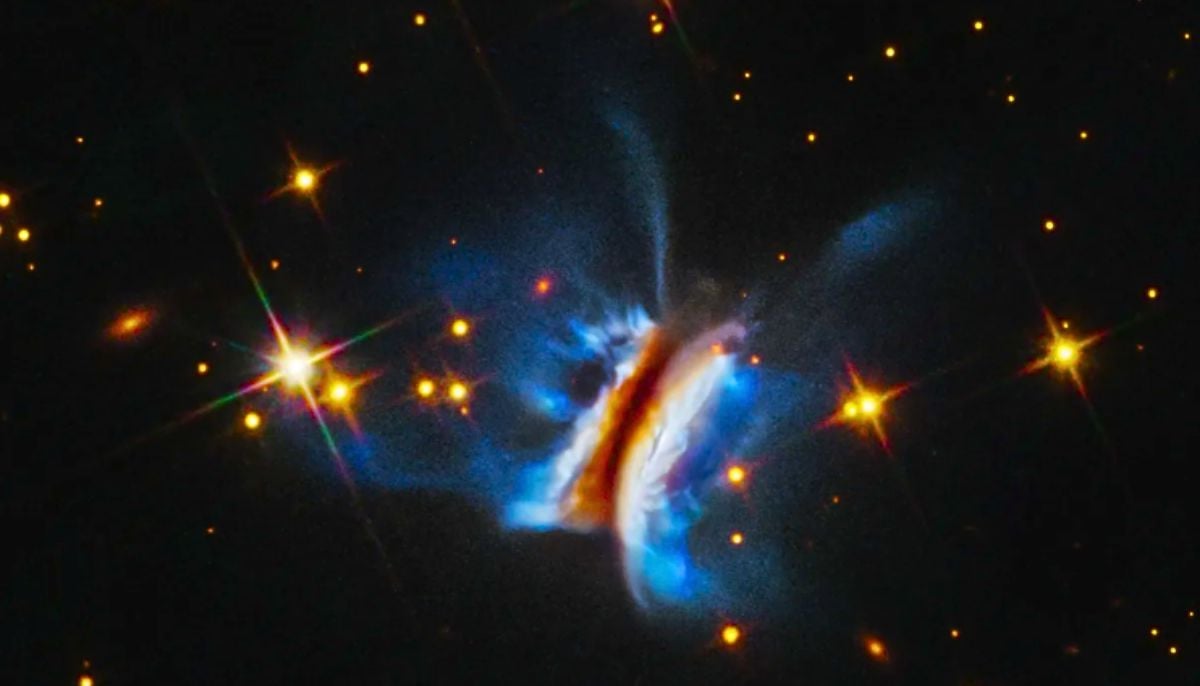
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope discovers ‘Dracula Disk', 40 times bigger than solar system
-
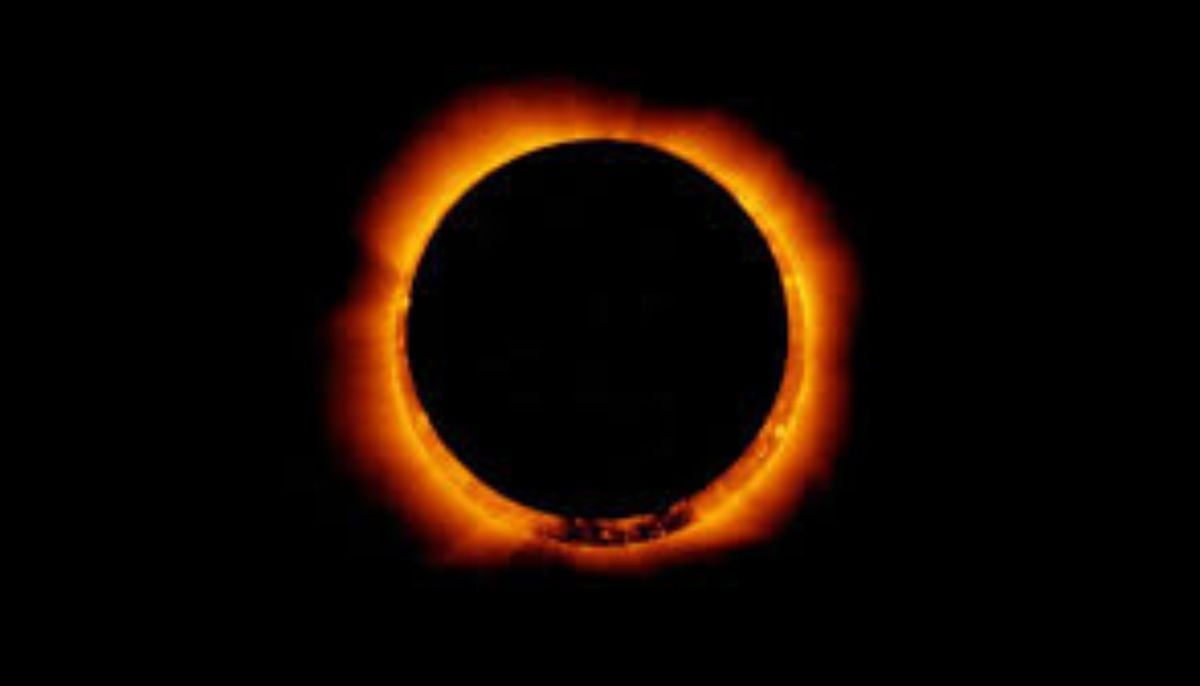
Annular solar eclipse 2026: Where and how to watch ‘ring of fire’
-
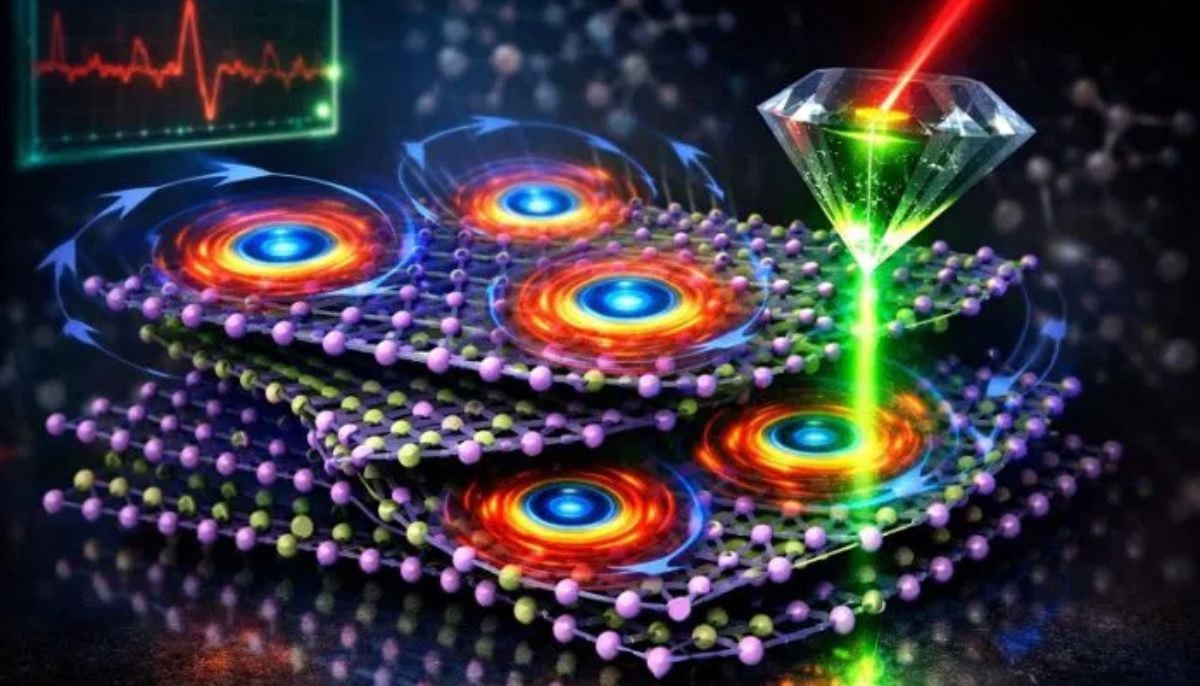
Scientists discover rare form of 'magnets' that might surprise you
-
Humans may have 33 senses, not 5: New study challenges long-held science
-
Northern Lights: Calm conditions persist amid low space weather activity
-
SpaceX pivots from Mars plans to prioritize 2027 Moon landing