WHO alert on Indian cough syrups blamed for deaths
WHO says products, manufactured by India's Marion Biotech, are "substandard"
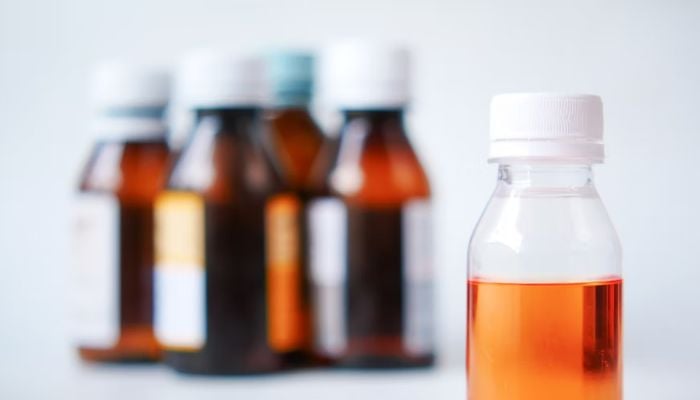
NEW DELHI: The World Health Organisation (WHO) has issued an alert warning against the use of two Indian cough syrups blamed for the deaths of at least 20 children in Uzbekistan.
WHO said the products, manufactured by India's Marion Biotech, were "substandard" and that the firm had failed to provide guarantees about their "safety and quality".
The alert, issued on Wednesday, comes after Uzbekistan authorities said last month at least 20 children died after consuming a syrup made by the company under the brand name Doc-1 Max.
India's health ministry subsequently suspended production at the company and Uzbekistan banned the import and sale of Doc-1 Max.
The WHO alert said an analysis of the syrup samples by the quality control laboratories of Uzbekistan found "unacceptable amounts of diethylene glycol and /or ethylene glycol as contaminants".
Diethylene glycol and ethylene are toxic to humans when consumed and can prove fatal.
"Both of these products may have marketing authorisations in other countries in the region. They may also have been distributed, through informal markets, to other countries or regions," WHO said.
The products were "unsafe and their use, especially in children, may result in serious injury or death", it said.
Marion Biotech officials could not be reached immediately for comment.
It is the second Indian drugmaker to face a probe by regulators since October when the WHO linked another firm's medicines to a spate of child deaths in Gambia.
Maiden Pharmaceuticals was accused of manufacturing several toxic cough and cold remedies that led to the deaths of at least 66 children in the African country.
The victims, mostly between five months and four years old, died of acute renal failure.
India launched a probe into Maiden Pharmaceuticals but later said the investigation had found the suspect drugs were of "standard quality".
-
Selena Gomez explains why she thought lupus was 'life-or-death'
-
How Kim Kardashian made her psoriasis ‘almost’ disappear
-
Nick Jonas gets candid about his type 1 diabetes diagnosis
-
Sir Jackie Stewart’s son advocates for dementia patients
-
5 celebrities you didn't know have experienced depression
-
Late James Van Der Beek inspires bowel cancer awareness post death
-
Bella Hadid talks about suffering from Lyme disease
-
Gwyneth Paltrow discusses ‘bizarre’ ways of dealing with chronic illness